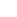Paludiculture on raised bog sites
Utilization of rewetted raised bogs: Sphagnum moss can be cultivated to produce high-quality growing media.
Peat moss cultivation

Peat moss (Sphagnum) cultivation is the growth of peat moss to be used as a renewable, environmentally friendly raw material.
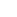
Sphagnum cultivation process:
- Seed: Crushed sphagnum mosses are used as seeds for establishing a peat moss culture, from which new moss grows.
- Establishment: peat moss fragments are spread evenly on a flat peat surface and covered with straw. Irrigation ditches provide a constant water supply for the growing moss.
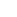
- The establishment of a uniform peat moss lawn can take place within 1.5 years.
- Growth: A uniformly high water level ensures good growth and maximum yields.
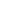
- Harvesting: During harvesting, the top of the peat moss is cut off. The sphagnum moss stems remaining on the surface continue to grow.
Drosera cultivation

Round-leaved sundew (Drosera rotundifolia) has been a sought-after medicinal plant for coughs and lung diseases since the 13th century. All parts of the plant, including the root can be used as a herbal medicine (Drosera herba).
As a result of drainage-based use, most European bogs are degraded and no longer provide habitat for sundew. Wild collections of the now rare and protected species are nowadays only possible at a small scale. Therefore, mainly Asian and African sundew species are used today, but they contain much lower concentrations of effective ingredients. The cultivation of sundew on rewetted, raised bogs is currently being tested and offers a new alternative for the procurement of Drosera herba from round-leaved sundew.
Sources & further information
- Flyer "Landwirtschaft auf nassen Hochmooren"
- Wichtmann, W., Schröder, C. & Joosten, H. (Hrsg.) 2016: Paludikultur – Bewirtschaftung nasser Moore. Schweizerbart, Stuttgart, 272 Seiten